Refuse-derived fuels (RDF) and secondary fuels (SRF)
Generating energy from waste
What are substitute fuels?
Refuse-derived fuels (RDF) or secondary fuels (SRF) are fuels that are obtained from solid, liquid or gaseous waste. This waste is processed to varying degrees for the respective purpose. The production of substitute fuels is used, among other things, to utilize recycled material (waste) that can no longer be recycled. The waste used for production comes from households, industry and commerce.
Alternative fuels as a solution
Today, we are faced with two challenges: On the one hand, the development that more and more waste is being produced in households, industry and commerce and, on the other hand, that these are simultaneously developing ever higher energy requirements.
Another key factor is the development of fossil fuels, as these are becoming increasingly scarce and expensive. In order to conserve natural fossil resources, substitute fuels have become a real economic alternative.
Production of substitute fuels
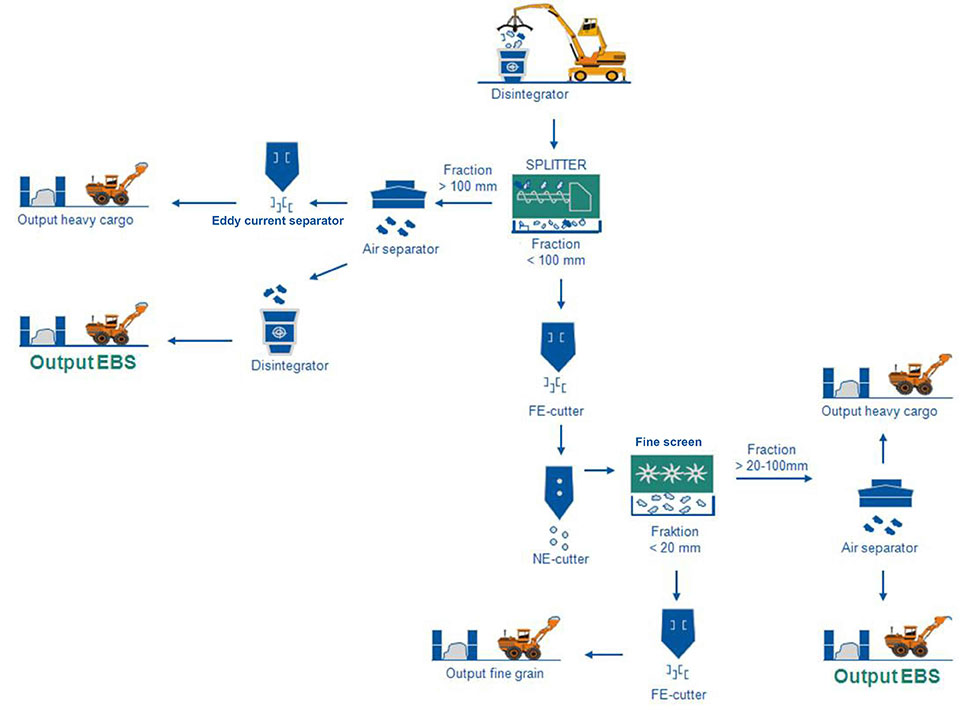
The processing of the material begins with the pre-sorting of the waste. The quality requirements are based on the requirements of the respective customer. The better and more selective the waste separation, the higher the quality of the substitute fuels. Processing plants with our patented SPLITTER technology ensure optimum pre-treatment of the waste to be processed.
You too can benefit from our experience, comprehensive advice and concept development through to after-sales service.
MULTISORT treatment plant
The plant was built in 2020. Every hour, 25-30 tons of commercial waste are processed into substitute fuel. The plant uses a SPLITTER Unit 625, an IFE double-deck screening plant, air separators, light material separators and bag filters, conveyor technology including reversing belts as well as FE and NF separation.
A well thought-out design enables different operating modes and therefore several output qualities. The pre- and post-shredder have been integrated into the GÜNTHER control technology included in the scope of delivery.
Production of substitute fuels
Materials for the production of RDF
RDF should only consist of 2D materials (e.g. film shreds) and should not contain any 3D materials (e.g. stones, glass, pieces of wood, etc.). For the production of substitute fuels, plastics are preferably used that have previously been pre-sorted from various types of waste.
The following materials are suitable for the production of substitute fuels:
Household waste, commercial waste, bulky waste, production waste, mixed packaging, packaging waste
Substitute fuel Calorific values
During processing, a distinction is made between medium calorific value (RDF - refuse derived fuel) and high calorific value (SRF - solid derived fuel), which means that the more materials with a high calorific value (e.g. film) are contained in the material, the higher the calorific value.
- High-calorie: calorific value often > 21 mJ/kg
- Medium caloric: calorific value often 12-16 mJ/kg
Processing of high-calorific RDF: A high process depth with many screening and separation steps is often required to obtain high-calorific RDF. Suitable material for high-calorific RDF is primarily lightweight packaging, production waste or pre-sorted material.
Processing of medium-calorific RDF: Various types of waste, such as household and commercial waste or bulky waste, are also suitable for the production of medium-calorific RDF. As the demand for medium-calorific RDF is usually higher than the demand for high-calorific material, different source materials with high and low calorific values are often mixed. In this way, a medium calorific value can be achieved and the entire amount of material can be processed at the same time.
As commercial waste often has a high calorific value and bulky waste a low calorific value, the materials are often mixed in order to process all materials.
Where are substitute fuels used?
RDF power plant
In a RDF power plant (steam power plant), medium or high calorific RDF is used to generate heat and energy. In RDF power plants, RDF with a size of 80 mm up to approx. 200 mm can be incinerated.
Cement plant
As the cement industry is a particularly energy-intensive sector, the use of substitute fuels is particularly suitable here. High-calorific fluff is also very suitable because it burns in the air when it is "shot" through the lance into the rotary kiln and does not cause any "false inclusions" in the clinker (molten rock in the rotary kiln).
High-calorific substitute fuel (also known as fluff) is used in the rotary kiln. This fluff has a high calorific value as it has undergone several processes due to the higher processing depth and consists almost exclusively of film shreds. 30% of the RDF is used in the rotary kiln and should therefore be high-calorific. Depending on the cement plant (between 2-20 tons per hour), high-calorific fluff with a size of up to 30 mm can be incinerated.
Medium-calorific RDF is used in the calciner (tower). The demand for medium-calorific RDF in the cement plant is oftenup to 70% of the total RDF quantity. Medium-calorific RDF can be burned in the calciner with a size of 80-100 mm.
Do you have questions about the production of substitute fuels?
Products from Anlagenbau Günther in use in the production of substitute fuel
At the beginning of the process chain is the SPLITTER
Thanks to its specific design and mode of operation, the SPLITTER is able to process large quantities of material and even large pieces of material, including unshredded material. This significantly reduces the load and wear on the downstream units. Example of substitute fuel processing with the SPLITTER as a process screen.
The SPLITTER can be used as a process screen directly after the shredder. Thanks to the roller conveyor effect, the SPLITTER is able to separate out films and 2D parts in the oversize grain. 3D material, cubic and heavy material falls through the screen and ends up in the undersize. This makes it possible to produce a high-calorific substitute fuel from waste that has not been pre-sorted and pre-treated. 2D materials such as films (e.g. yellow bags), which have a high calorific value, are separated in the oversize grain. This enables these to be processed into high-quality fluff instead of only producing medium-calorific RDF.
Even if your company does not plan to process the oversize grain into high-calorific RDF, it can still be used economically and collected for further processing in another company that uses it to produce high-calorific substitute fuel.
The quality of the screening of medium and high-calorific material remains constant over the entire screening period thanks to the self-cleaning effect of the spiral shafts.
The SPLITTER as a pre-separator
In southern countries in particular, there is no strict separation with organic waste garbage cans, yellow bags, etc., so there is often a lot of organic material in the waste. Here, the SPLITTER acts as a pre-separator, separating out the organic and mineral material in the undersized particles and the valuable material in the oversized particles can be separated for RDF production.
Recommended SPLITTER for substitute fuel production
With its compact screen deck, the stationary SPLITTER UNIT is particularly suitable as the first step in a process chain for processing solid waste such as lightweight packaging, commercial and household waste, scrap metal, slag, waste wood and much more.

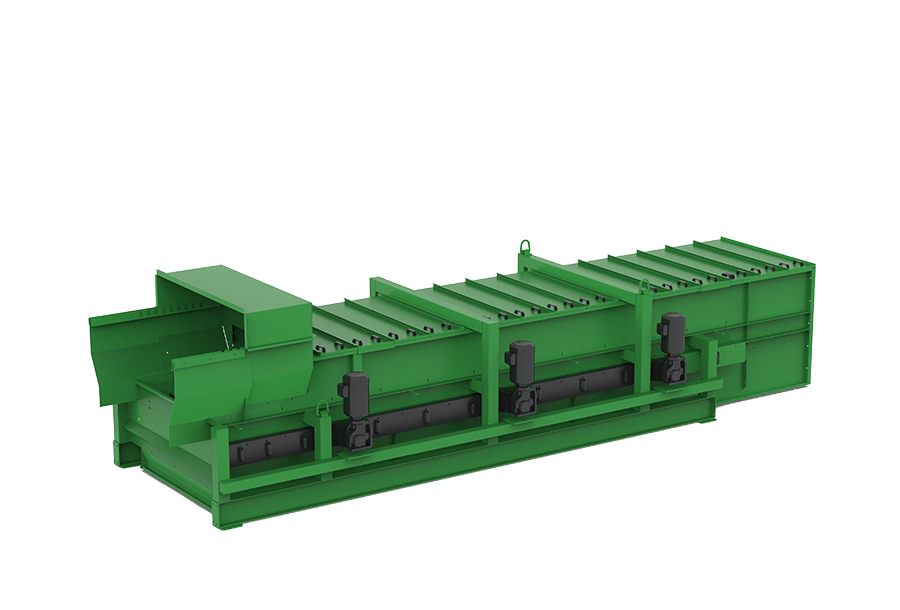
The star screen at the end of the process chain
At the end of the process chain, the star screen is often used as a safety screen/polishing screen. This ensures that there are no "fish" in the material before incineration and that any incorrect inclusions in the clinker are not caused during incineration. The star screen reliably sieves out unwanted long pieces through the fingers of the star and the rotating movement. The star screen is therefore a reliable quality assurance tool in the process chain.
- SSF = Star Screen Fine:processes high-calorific substitute fuels up to 30 mm
- SSC = Star Screen Course: prepares medium-calorific substitute fuel up to 80-100 mm
Advantages of connecting a star screen downstream in the process chain:
- High throughput
- Quality-assured goods
- Relief of the secondary shredding
- Less energy consumption and wear on the shredder
Advantages for EBS suppliers:
- The higher the quality of the goods, the higher the revenues that can be achieved. This may mean better marketing opportunities.
Advantages for cement conditioners:
- With a separate star screen, goods of lower quality can also be accepted and the quality of the RDF can be ensured.
Recommended Multistar star screen for refuse derived fuel production
The MULTISTAR 2-SE star screen is an easy-to-integrate solution thanks to its compact design. A modular system and options such as substructure, feed dosing hopper with feed and discharge belts, air separation, etc. guarantee exact adaptation to your customer requirements.
More about the MULTISTAR 2-SE Special
Do you have questions about SPLITTER or star screen?
Frequently asked questions about refuse derived fuels, star screens and SPLITTER
- Star sieve: For precise fine sieving, safety sieve, exact sieve, police sieve
- SPLITTER: Pre-screening of coarse, bulky material to differentiate it for the process chain
- Flowerdisc: For clean input material that tends to wrap, primarily household waste
Every project and source material is different. Contact us now for advice on the use of the different screen variants.
- Our screens are able to screen material in the size range 60-250 mm
- SPLITTER-Technology is sold directly by Anlagenbau Günther
- Star screen technology and disk screens are distributed exclusively by our partner Komptech
Your contact person